- Curator Danbi
- Tips for Social Media - IT Tech / AI News about Creators from World
Aviation safety is determined by the interaction of many complex factors. This article aims to provide a broad understanding of aviation safety by in-depth analysis of three important topics: bird strike, go-around, and runway surrounding facilities.

2024 Jeju Air Muan Airport Accident: Potential Causes
1. Bird Strike: Scientific Analysis and Re-examination of Severity
Bird strike is not simply a physical collision between a bird and an aircraft; it is a phenomenon involving a complex interplay of knowledge from various fields such as aerodynamics, ecology, and engineering.
- In-depth Study of Collision Physics:
- Impulse Calculation: In addition to the law of conservation of momentum, the energy conversion (kinetic energy → deformation energy) occurring during the collision must be considered. The material of the colliding bodies, the angle of collision, and the relative speed affect the impulse.
- Cavitation Effect: When a high-speed rotating engine blade collides with a bird, cavitation, a phenomenon in which bubbles are generated inside a liquid (such as engine oil), can occur, causing additional damage.
- Ecological Factors:
- Migratory Bird Routes: By analyzing the migratory bird routes around airports, it is possible to predict the risk period of bird strikes and strengthen preventive measures.
- Bird Behavior Patterns: By studying bird flight habits, flocking behavior, and feeding activities, effective bird control methods should be developed.
- Types of Aircraft Damage:
- Engine Damage: It manifests in various forms, such as fan blade breakage, compressor damage, and combustor damage, and in severe cases, it can lead to engine failure.
- Structural Damage: It occurs on the wings, fuselage, and tail, affecting the aerodynamic performance of the aircraft and impairing flight stability.
- Electronic Equipment Damage: It can cause malfunctions by causing direct impact or electromagnetic interference to electronic equipment such as radar and communication equipment.
2. In-depth Analysis of the Relationship between Bird Strike and Landing Gear
The relationship between bird strike and landing gear is manifested through indirect influence rather than a direct causal relationship.
- Vulnerability of Hydraulic Systems: If hydraulic lines, pumps, and valves are damaged due to a bird strike, it can affect not only the operation of the landing gear but also other hydraulically operated devices such as the flight control system and braking system.
- Complexity of Electrical/Electronic Systems: The landing gear of modern aircraft is operated by complex electronic devices such as electrical signals, sensors, and computer control systems. If some of these systems are damaged due to a bird strike, serious problems can occur in the landing gear operation.
- Complex System Failures: If a bird strike affects multiple systems simultaneously, cascading problems can occur in the landing gear operation along with the failure of other systems (e.g., flaps, spoilers, brakes, etc.) necessary for landing gear operation.
2-1. Analysis of the Possibility of Landing Gear Malfunction due to Poor or Negligent Maintenance
Poor and negligent maintenance can be a major cause of landing gear malfunction, separate from bird strikes. This can occur in several ways:
- Non-compliance with Maintenance Instructions: Failure to properly follow the maintenance instructions provided by the aircraft manufacturer or regulatory agencies can lead to inadequate inspection and replacement of landing gear components, resulting in malfunctions. For example, problems can arise from failure to properly check for contamination or lack of hydraulic fluid for landing gear operation, deterioration of hydraulic hoses, or wear of locking devices.
- Component Defects and Use of Defective Parts: Failure to detect component defects during maintenance or the use of unapproved defective parts can cause serious problems in the operation of the landing gear. In particular, since the landing gear is a component that receives a large load during takeoff and landing, quality control of parts is very important.
- Human Error: Human errors such as incorrect installation of parts or omission of connections due to mistakes by maintenance personnel can occur. Such errors can directly affect the landing gear operating system and lead to accidents.
- Negligence in Inspection: If the landing gear system is not thoroughly inspected during regular inspections, problems that could be detected and addressed in advance may be missed. For example, if defects in the landing gear operating switch, damage to the wiring, or malfunction of the sensor are not detected, the landing gear may fail to operate during takeoff or landing.
- Poor Record Management: If maintenance records are not properly maintained, past problems or maintenance history cannot be properly understood, and the same problems may be repeated. Also, the replacement cycle of parts may be missed, and timely replacement may not be made.
Jeju Air is an LCC airline, and maintenance issues due to low profitability are also emerging, so we need to watch the investigation by the relevant authorities.
3. Go-around: The Importance of Skilled Judgment and Technique of Pilots
A go-around is not simply giving up on landing, but a procedure that requires high piloting skills and accurate judgment to ensure safety.
- Criteria for Go-around Decision:
- Deviation from Stable Approach Path: If the landing path is unstable or deviates from the runway centerline.
- Sudden Change in Weather Conditions: If sudden gusts, deterioration of visibility, etc., occur just before landing.
- Changes in Runway Conditions: If obstacles appear on the runway or if a preceding aircraft fails to clear the runway.
- Air Traffic Control Instructions: If a go-around is required according to instructions from the control tower.
- Details of the Go-around Procedure:
- Increase Power: Engine power must be increased quickly and accurately.
- Pitch Control: The nose must be raised while maintaining the appropriate climb angle.
- Flaps and Landing Gear Operation: Flaps and landing gear must be operated in the prescribed order.
- Air Traffic Control Communication: The control tower must be informed of the go-around and instructions must be received.
- Importance of Go-around Training: Pilots must master the go-around procedure in various situations through simulator training.
4. Diversity and Function of Runway Surrounding Facilities
Various facilities are installed around the runway, and each function plays an important role in aviation safety and efficient airport operation.
However, since this accident occurred in a large open space beyond the wall around the runway, it is predicted that there would have been no explosion or fire due to the collision if there had been no wall. We need to carefully consider the necessity of installing such facilities around the airport.
Even before the wall, there is a very firmly installed structure (presumed to be a localizer antenna). Since the aircraft was unable to pass through this structure after the belly landing, causing a tremendous explosion and significant damage to the aircraft, the reasons for installing this structure here should also be verified.
2024 Jeju Air Muan Airport Accident: Potential Causes - Poor Maintenance vs. Bird Strike, Landing Gear, and Wall Collision After Emergency Landing
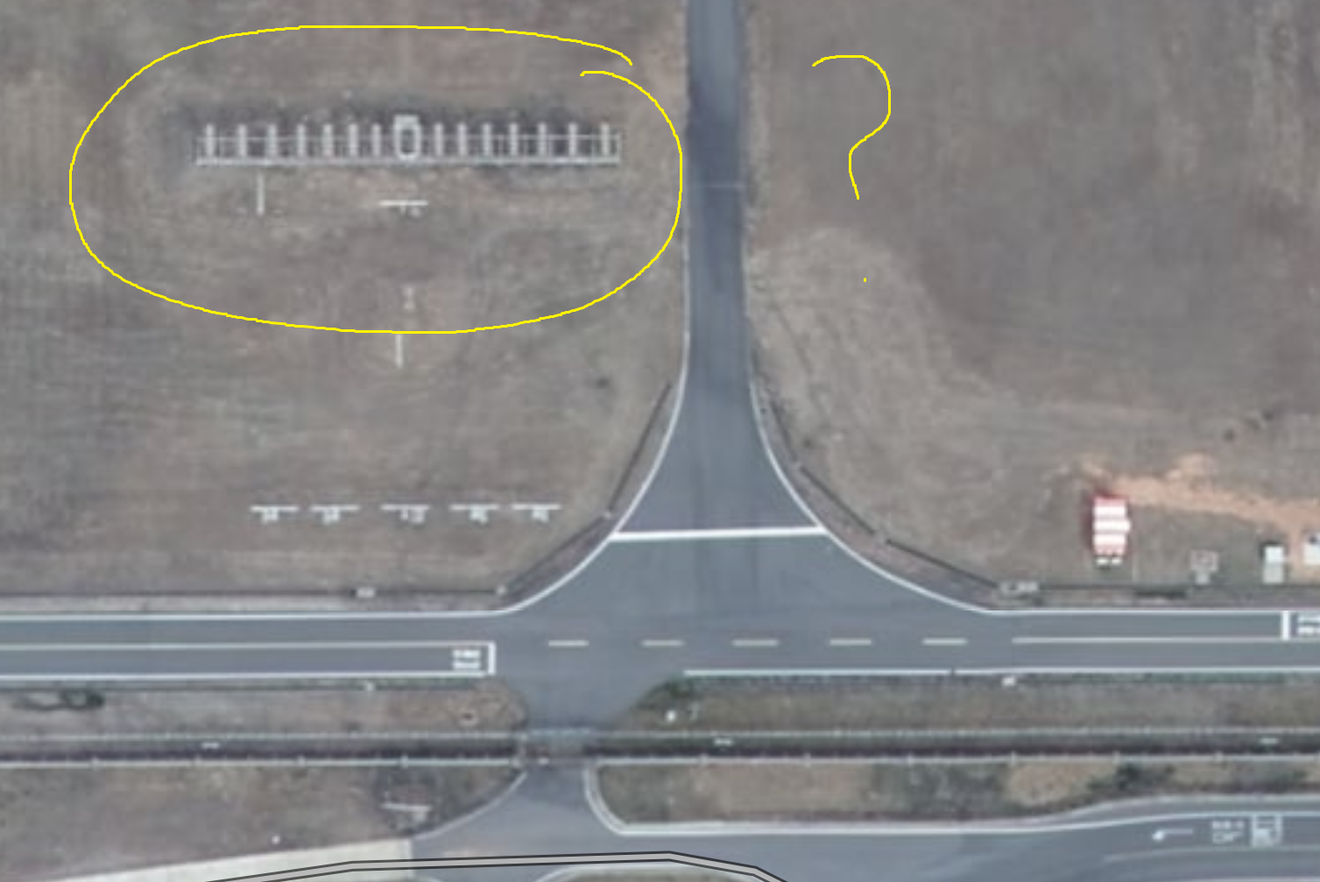

Presumed to be a localizer antenna
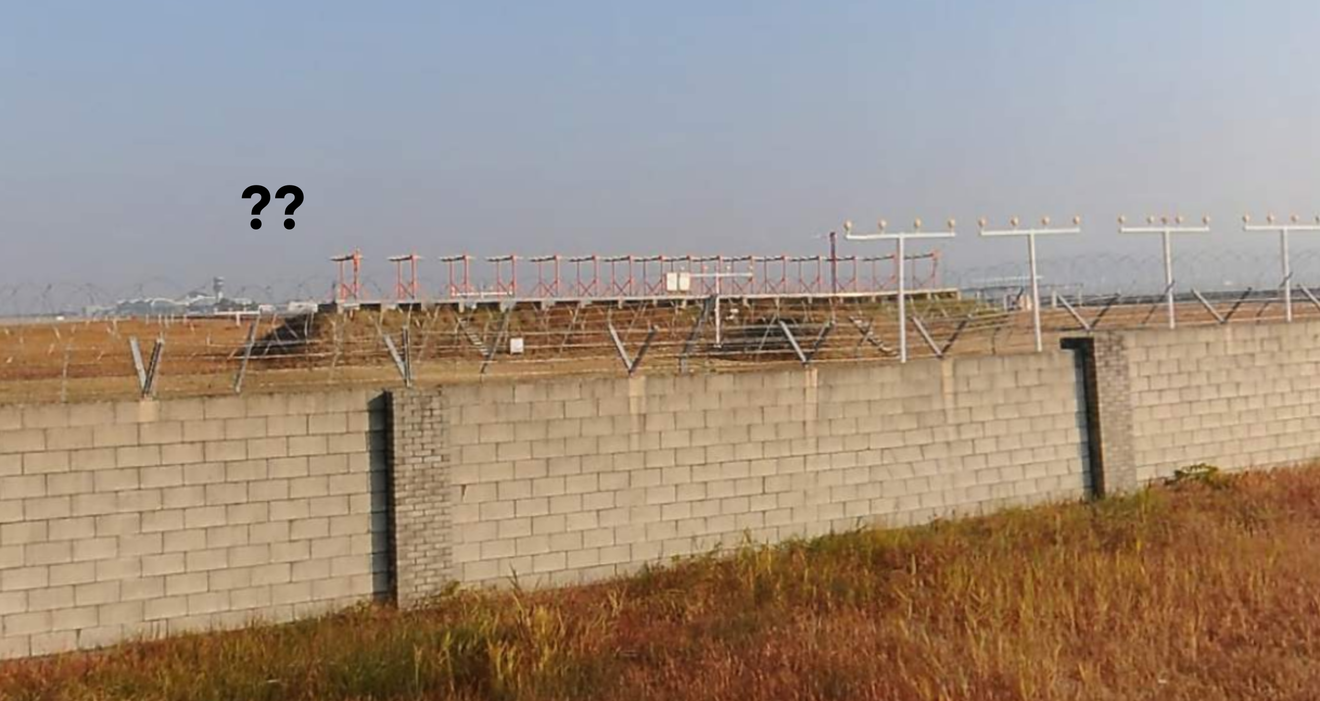

Facility presumed to be a localizer antenna
- Expanded Function of Walls (Fences):
- Noise Reduction: It also plays a role in reducing the spread of airport noise to surrounding areas.
- Enhanced Security: It can be used to build a more effective security system by linking it with advanced detection equipment.
- Lead-in Lighting: It helps pilots easily identify the runway at night or in bad weather.
- Runway Centerline Lights: Lights installed along the center line of the runway to help aircraft maintain the center of the runway during landing.
- Touchdown Zone Lights: Lights indicating the landing point of the runway to help determine the exact landing point.
- Runway End Lights: Lights indicating the end point of the runway to prevent runway excursions.
- Localizer: Ground-based navigation safety facility that emits radio waves from one end of the runway to accurately guide aircraft to the runway centerline during landing.
Another Information of this Blog

Comments0